The researchers used scanning electron microscopy and compositional analysis (EDS) at our facility – Sydney Microscopy and Microanalysis – to understand the surface area and structure of the materials. These properties are strongly related to the potential energy storage capacity. Along with this, X-ray diffraction was used to observe it’s crystal structure and transmission electron microscopy to demonstrate the amorphous structures and regions of the fruit that had been converted to graphite.
“Using durian and jackfruit purchased from a market, we converted the fruits’ waste portions (biomass) into super-capacitors that can be used to store electricity efficiently,” said Associate Professor Gomes.
“Using a non-toxic and non-hazardous green engineering method that used heating in water and freeze drying of the fruits’ biomass, the durian and jackfruit were transformed into stable carbon aerogels — an extremely light and porous synthetic material used for a range of applications. Carbon aerogels make great super-capacitors because they are highly porous. We then used the fruit-derived aerogels to make electrodes which we tested for their energy storage properties, which we found to be exceptional.”
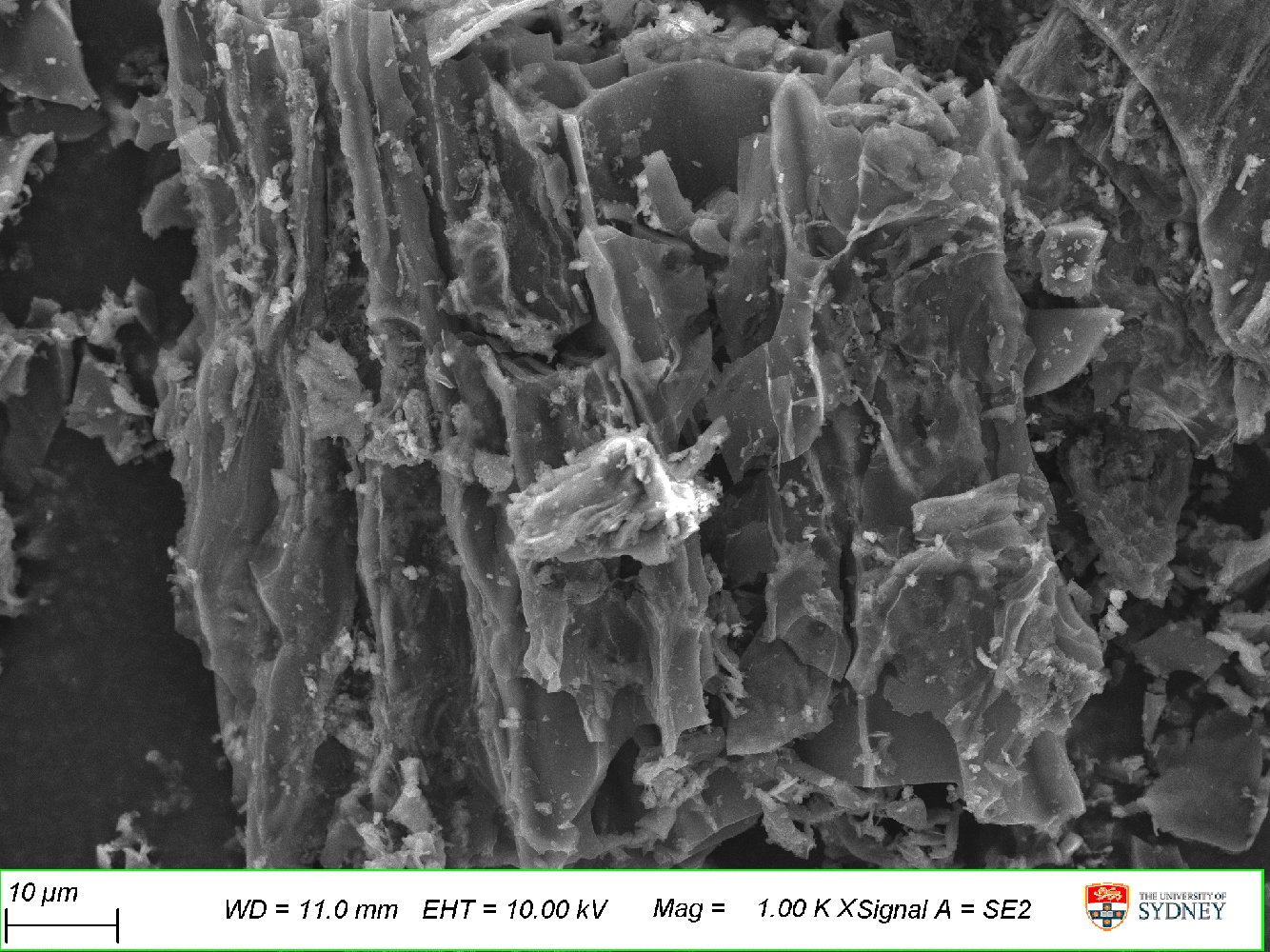

Scanning electron micrograph of durian aerogel side wall
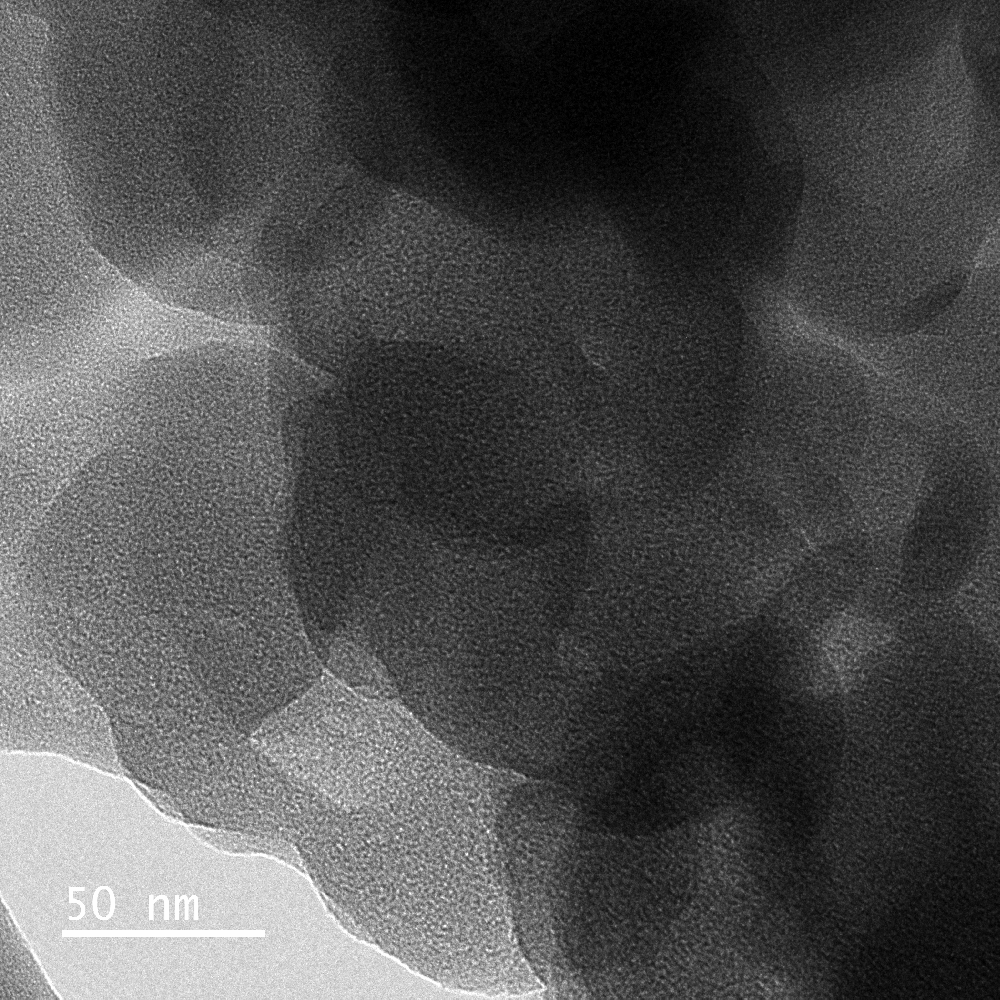
Transmission electron micrograph of durian based aerogel
“Super-capacitors are like energy reservoirs that dole out energy smoothly. They can quickly store large amounts of energy within a small battery-sized device and then supply energy to charge electronic devices, such as mobile phones, tablets and laptops, within a few seconds,” said Associate Professor Gomes.
“Compared to batteries, super-capacitors are not only able to charge devices very quickly but also in orders of magnitude greater charging cycles than conventional devices.
“The current super-capacitors are made from activated carbon which are nowhere near as efficient as the ones prepared during this project.”
“Durian waste was selected based on the excellent template nature provides for making porous aerogels,” said Associate Professor Gomes.
“The durian and jack-fruit super-capacitors perform much better than the materials currently in use and are comparable, if not better, than the expensive and exotic graphene-based materials.
“Durian waste, as a zero-cost substance that the community wants to get rid of urgently due to its repulsive, nauseous smell, is a sustainable source that can transform the waste into a product to substantially reduce the cost of energy storage through our chemical-free, green synthesis protocol.”
“We have reached a point where we must urgently discover and produce ways to create and store energy using sustainably-sourced materials that do not contribute to global warming,” said Associate Professor Gomes.
“Confronted with this and the world’s rapidly depleting supplies of fossil fuels, naturally-derived super-capacitors are leading the way for developing high efficiency energy storage devices.”
March 26, 2020